June is National Men’s Health Awareness Month, a great time to bring your attention to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), one of the most common health problems men face as they age. According to the National Institutes of Health, BPH affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80.
While BPH is a benign condition, unrelated to prostate cancer, it can greatly affect a man’s quality of life. If left untreated, BPH can lead to permanent bladder damage.
What is BPH?
BPH is caused by a non-cancerous enlargement of the male reproductive gland, known as the prostate. The prostate surrounds the urethra, the tube at the neck of the bladder that carries semen and urine. When the prostate enlarges, it blocks the urethra causing urinary problems.
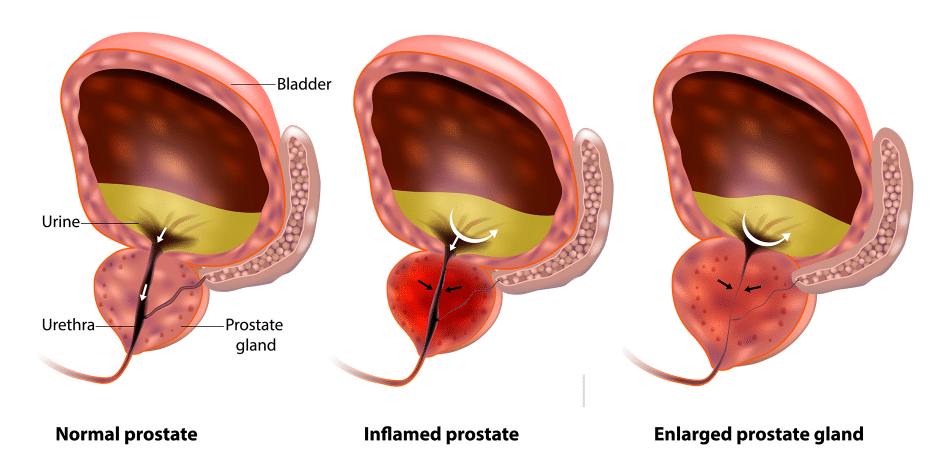
What are the Symptoms?
An enlarged prostate can cause symptoms such as the need to urinate frequently, trouble emptying the bladder, urgency in urination, difficulty or delay in starting to urinate, and weak or slow urine flow. Less common symptoms include urinary tract infections, blood in the urine and the inability to urinate.
The size of your prostate doesn’t necessarily determine the severity of your symptoms. Some men with only slightly enlarged prostates can have significant symptoms, while other men with very enlarged prostates can have only minor urinary symptoms.
Does BPH increase your Risk of Prostate Cancer?
Though BPH does not increase your chance of getting cancer, many of the early signs are the same.
What causes BPH?
The exact scientific cause of BPH is yet to be determined but hormonal changes associated with aging are believed to be a major factor. Other risk factors include family history, heart disease, obesity and diabetes.
Are there ways to lower the risk of BPH?
Research shows that regular exercise mitigates the risk of BPH. In a number of studies men who were more physically active were less likely to suffer from BPH. Even low to moderate intensity physical activity, such as walking regularly at a moderate pace, yielded benefits.
Diagnosis and Treatment of BPH
We encourage you to download the Mason City Clinic’s recently revised Health Guide on BPH. It includes information on diagnosing and treating this condition including new minimally invasive treatment options that have high success rates and low risk of side effects.
Lifestyle Tip to Reduce Symptoms of BPH
Keep a healthy weight and exercise regularly.
* Take care to empty your bladder completely every time you urinate.
* Nervousness and tension can cause you to urinate more frequently. Reduce stress by exercising regularly and practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation.
* Discuss all the medications you are talking with your doctor – including over-the-counter drugs. Some may be contributing to the problem, and it is possible that there are alternatives.
* Avoid fluids at night, particularly caffeine and alcohol, which affect the muscle tone of the bladder and stimulate the kidneys to produce urine.
If you are suffering from symptoms of BPH, it is important that you get checked by a urologist to determine the cause of the problem and rule out more serious conditions. Our board-certified urologists can be reached at 641.494.5280.
Up-to-date. Down-to-earth. Close to home. Lots of great reasons to make Mason City Clinic
your first choice for all your family’s specialty healthcare needs.
250 S. Crescent Drive, Mason City, IA 50401
Tel: 641.494.5200
Toll Free: 800-622-1411
Fax: 641.494.5403